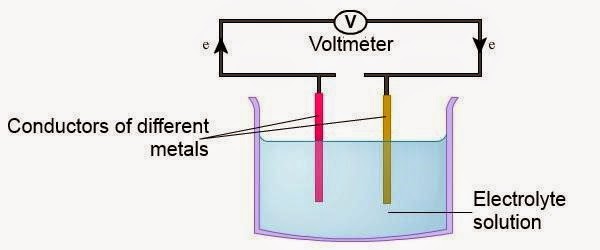
■ Voltaic cell
| ► | An electrochemical cell that derives electrical energy from reaction taking place within the cell. |
| ► | Consists of two different metal electrodes. | ||||||||||
| ► | Connected to the end of the wire and the other end dipped into an electrolyte solution. | ||||||||||
| ► | Potential difference generated depends on the difference in the position of the metal used in the electrochemical series.
 |
||||||||||
| ► |
Electric current flows in the opposite direction of electrons flow. |
| ► | Zinc located higher in the electrochemical series(more electropositive) will act as the negative terminals. | |||||||||||||
| ► | Copper located lower in the electrochemical(less electropositive) will act as the positive terminal. | |||||||||||||
| ► |  |
|||||||||||||
| ► |
Electric current flow in the opposite direction of electrons flow. Overall ionic equation : Zn + CU2+ → Zn2+ + Cu |
■ Daniel cell
| ► | Consists of two different metal electrodes immersed in two separate electrolyte solutions. | ||||||||||
| ► | Electrolyte solution can be separated either by a porous pot or a salt bridge. | ||||||||||
| ► | Function of porous pot or salt bridge: to separate two electrolyte solutions but allow ions to pass through to complete a circuit. | ||||||||||
| ► | Chemical energy → electrical energy.
Electric current flows in the opposite direction of electrons flow. |
Electrolyte solution separated by a salt bridge.
 |
|||||||||
Electrolyte solution separated by a porous pot.
 |
|||||||||
Electrolyte solution separated by a salt bridge(U-tube).
 |
|||||||||
Chemical reactions:
Electric current flow in the opposite direction of electrons flow. Overall ionic equation: Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) |
■ Voltaic cell can be divided into two types:
| ► | Primary cells : non-rechargeable cells | |
| ► | Secondary cells : rechargeable cells |
 |
► | Positive terminal : carbon rod 2MnO2(s) + 2NH4+(aq) + 2e- → Mn2O3(s) + 2NH3(g) + H2O(l) |
| ► | Negative terminal : zinc Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e- |
|
| ► | Electrolyte: Mixture of ammonium chloride and zinc chloride. | |
| ► | Advantages: light and supplies constant current. | |
| ► | Disadvantages: not long-lasting and not rechargeable | |
 |
► | Positive terminal : Manganese(IV) oxide 2MnO2(s) + H2O(l) + 2e- → Mn2O3(s) + OH-(aq) |
| ► | Negative terminal : zinc Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e- |
|
| ► | Electrolyte: Mixture of ammonium chloride and zinc chloride. | |
| ► | Advantages : long-lasting and supplies high voltage than dry cell for long period. | |
| ► | Disadvantages : expensive than dry cell and not rechargeable. | |
 |
► | Positive terminal : Mercury(II) oxide HgO(s) + H2O(l) + 2e- → Hg(l) + 2OH-(aq) |
| ► | Negative terminal : zinc Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e- |
|
| ► | Electrolyte: Mixture of zinc hydroxide and potassium hydroxide solution. | |
| ► | Advantages : long-lasting and supplies constant current. | |
| ► | Disadvantages : not rechargeable. |
 |
► | Positive terminal: Lead(IV) oxide PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e- → Pb2+(aq) + 2H2O(l) |
| ► | Negative terminal : lead Pb(s) → Pb2+(aq) + 2e- |
|
| ► | Electrolyte: Dilute sulphuric acid. | |
| ► | Advantages : rechargeable and supplies high voltage for long period. | |
| ► | Disadvantages : heavy, expensive and use electrolyte which corrodes easily. | |
 |
► | Positive terminal: Nickel(IV) oxide NiO2(s) + 2H2O(l) + 2e- → Ni(OH)2(s) + 2OH- |
| ► | Negative terminal : cadmium Cd(s) + 2OH- → Cd(OH)2(s) + 2e- |
|
| ► | Electrolyte: Potassium hydroxide. | |
| ► | Advantages : long-lasting, rechargeable and concentration of its electrolyte does not change | |
| ► | Disadvantages : expensive |
■ Similarities of electrolytic cell and voltaic cell
| ► | Consists of an anode and a cathode [a positive terminal and a negative terminal] | |
| ► | Contains an electrolyte | |
| ► | Chemical reaction involves donating or receiving electrons | |
| ► | Positive and negative ions move to the electrodes in the electrolyte | |
| ► | Electrons move from the anode to cathode [negative terminal to positive terminal in the outer circuit] |
| Differences | Electrolytic cell | Voltaic cell |
| Cell structure |  |
 |
| Made of | Carbon or different/same metal immersed in the electrolyte | Two different metals immersed in the electrolyte |
| Electric current | Produces chemical reaction | Produced by chemical reaction |
| Energy changes | Electrical energy to chemical energy | Chemical energy to electrical energy |
| Cathode | Cations receive electrons | Electrons are accepted |
| Anode | Anions release electrons | Electrons are released |
| Requirement of battery | Uses battery | Does not use battery |
| ⇲ For exercise(objective and subjective), download for free on Android OS. | ||
 |
 |
|


No comments:
Post a Comment